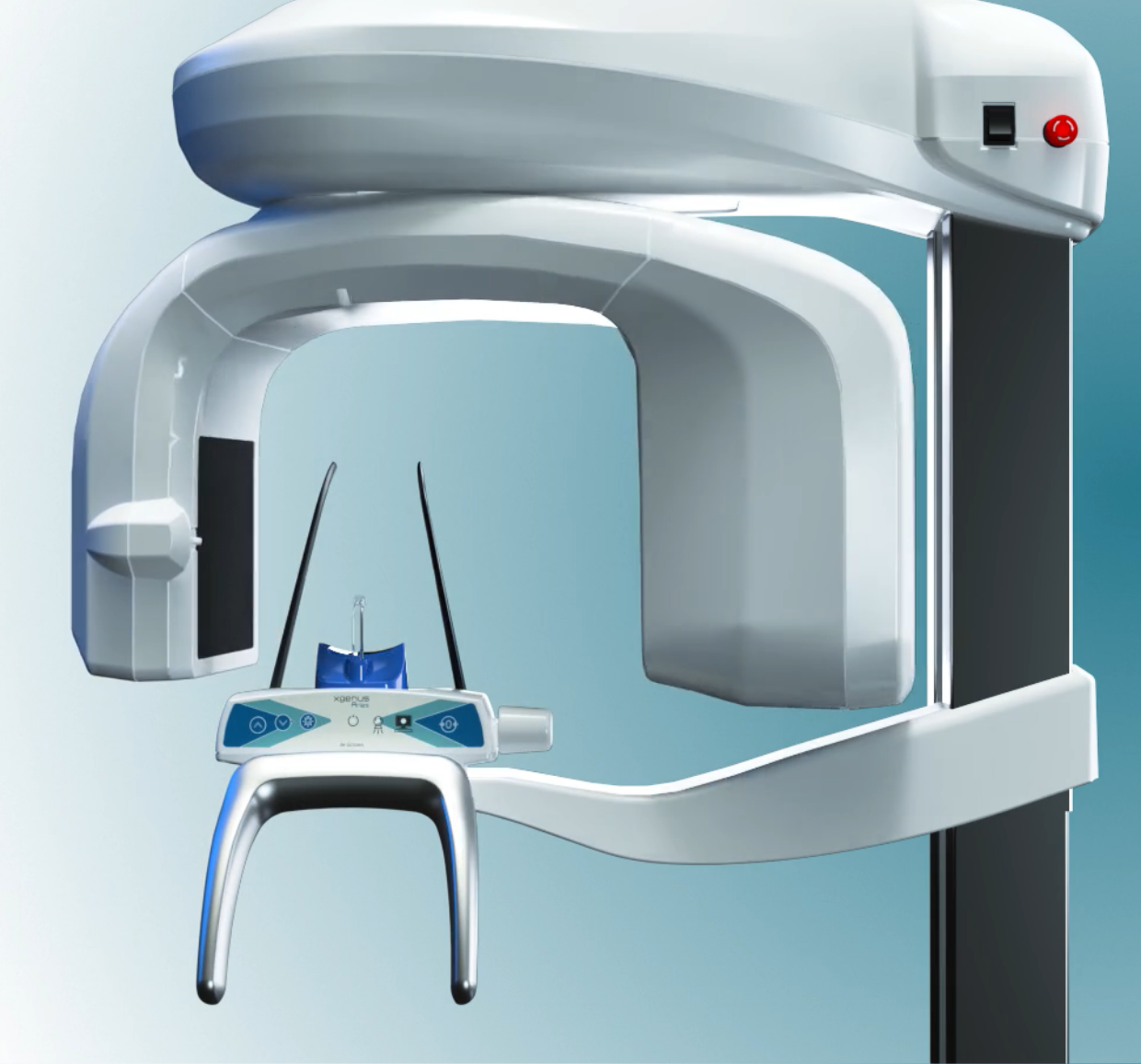
Più potenza al 3D. Più energia al tuo workflow. Più valore ai tuoi risultati. ...


11-02-2020
CONVENTIONAL AC GENERATORS
The mains alternating current (50 Hz) is applied to a circuit (basically a step-up transformer) which elevates it from 230V to 70.000V (70kV).
The high voltage (still at 50Hz) is applied to a rectifier circuit which:
- Eliminates the negative portion of the waves (half wave rectifier), or
- Converts the negative half-waves into positive (full wave rectifier)
- The portion of wave useful for image formation is limited to the “crest”
- All the rest doesn’t produce film blackening, but it is noxious for the patient
HIGH FREQUENCY AND DC GENERATORS
- The HF generator employs a specific circuitry (INVERTER) which generates a waveform of much higher frequency than the mains
- Typical operating frequency of an HF generator is in the order of several tens of kilohertz (kHz)
- A specific circuits “flattens” the crests of the waves to further increase the amount of useful radiation
- Such almost flat waveform is called “constant potential”, or DC
COMPARISON OF WAVEFORM
DC GENERATOR
If the ripple is smaller than 4%, the IEC standards allow to give the generator the “constant potential” or DC attribute.
HF TECHNOLOGY ADVANTAGES
- Tubehead more compact and lighter, because the high voltage transformer is smaller
- Patient dose reduced by 25%, because the “soft” X-ray portion is reduced
- kV value can be lower (60 kV instead of 70) because the entire waveform is “useful” to produce image
- Complete line voltage fluctuation insensibility
- Exposure times shorter

Più potenza al 3D. Più energia al tuo workflow. Più valore ai tuoi risultati. ...
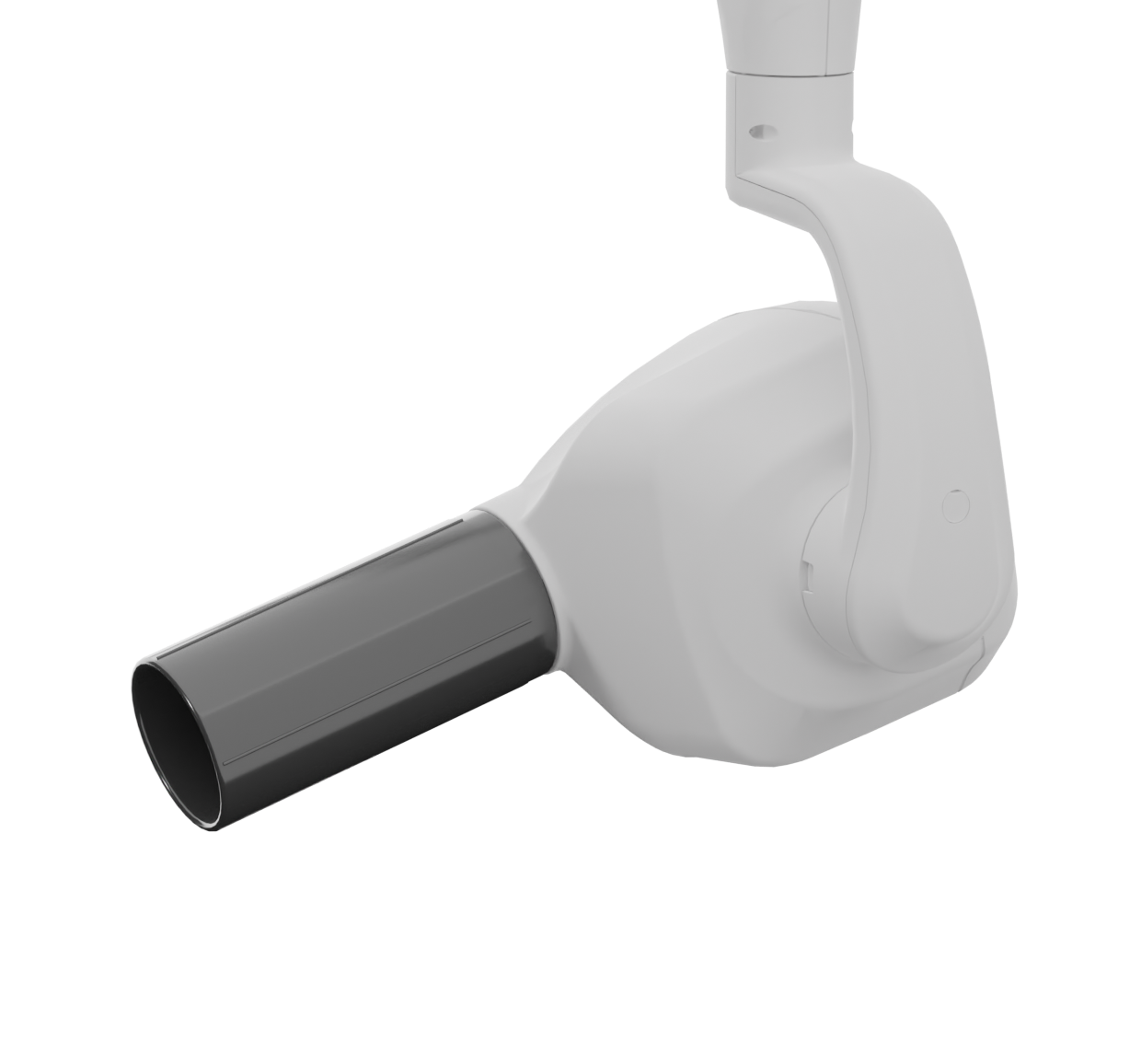

CONVENTIONAL AC GENERATORS The mains alternating current (50 Hz) is applied to a circuit (basically a step-up transformer) which elevates it from 230V to 70.000V (70kV). The high voltage (still at 50Hz) is applied to a rectifier circuit w...